The dreaded rat lungworm—a parasite with a penchant for rats and slugs that occasionally finds itself rambling and writhing in human brains—has firmly established itself in the Southeast US and will likely continue its rapid invasion, a study published this week suggests.
The study involved small-scale surveillance of dead rats in the Atlanta zoo. Between 2019 and 2022, researchers continually turned up evidence of the worm. In all, the study identified seven out of 33 collected rats (21 percent) with evidence of a rat lungworm infection. The infected animals were spread throughout the study's time frame, all in different months, with one in 2019, three in 2021, and three in 2022, indicating sustained transmission.
Although small, the study "suggests that the zoonotic parasite was introduced to and has become established in a new area of the southeastern United States," the study's authors, led by researchers at the University of Georgia College of Veterinary Medicine, concluded. The study was published Wednesday in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases.
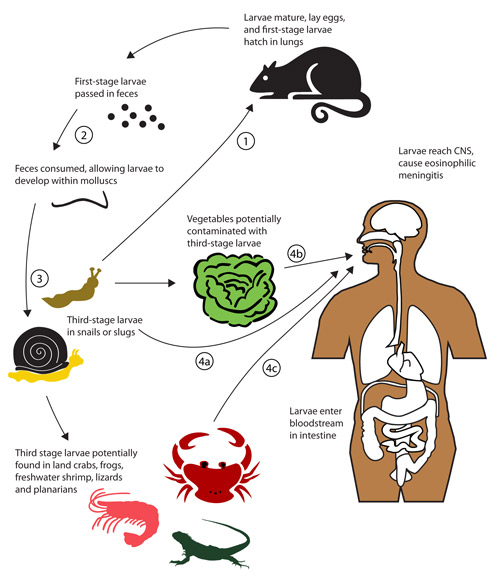
The finding is concerning given the calamitous infection the rat lungworm, aka Angiostrongylus cantonensis, can cause in humans. The parasitic nematodes are, as their name suggests, typically found in rats. But they have a complicated life cycle, which can be deadly when disrupted.
Sickening cycle
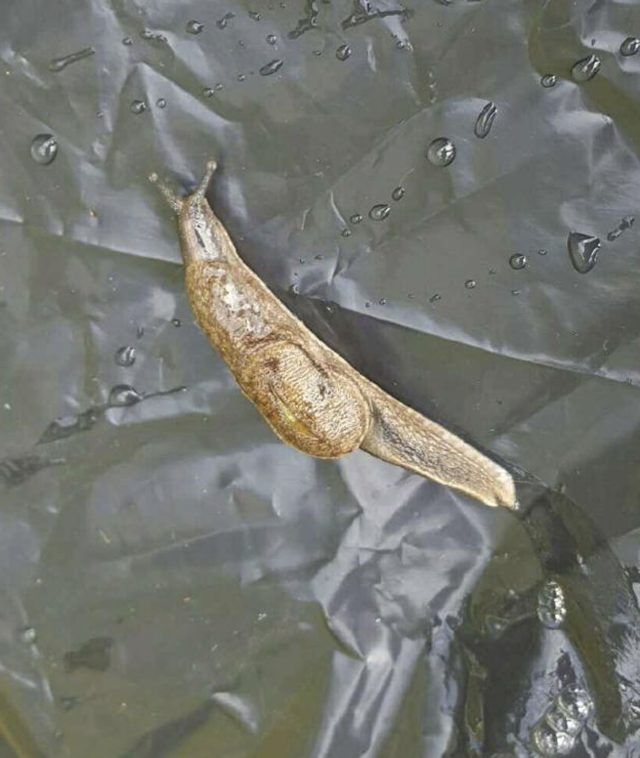
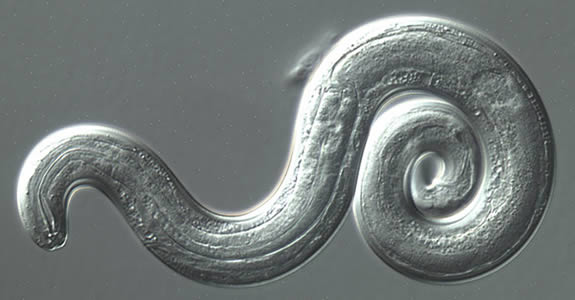
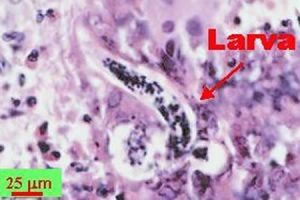
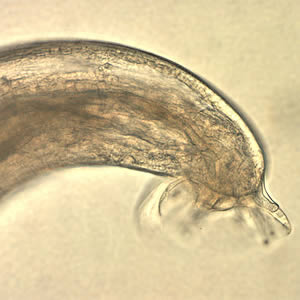
Normally, adult worms live in the arteries around a rat's lungs—hence rat lungworm. There, they mate and lay eggs. The worm's larvae then burst out of the lungs, get coughed up by the rat, and are swallowed and eventually pooped out. From there, the larvae are picked up by slugs or snails. This can happen if the gastropods eat the rat poop or if the ravenous larvae just bore into their soft bodies. The larvae then develop in the slugs and snails, which, ideally, are eventually eaten by rats. Back in a rat, the late-stage larvae penetrate the intestines, enter the bloodstream, and migrate to the rat's central nervous system and brain. There they mature into sub-adults then migrate to the lungs, where they become full adults and mate, thus completing the cycle.



 Loading comments...
Loading comments...
